This chapter explains the molding process, which is closely related to the quality of the molded products. It also describes the key aspects of quality improvement.
Quality of Molded Parts
Injection molding is a straight forward and economical molding method that allows for mass-production of complex-shape moldings to high precision standards.
The quality of the molded parts is largely determined by the performance of the injection-molding machine as well as by the precision and the function of the mold.
It is also influenced greatly by the molding material. Various combined factors involve molding production; a high-quality molding will be achieved upon good condition of all elements.
The following are the specific factors:
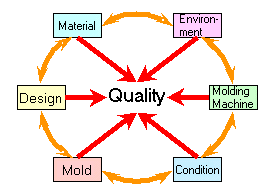 Material
Material
Type, Price, Physical properties
Design
Dimensions, Dimension tolerances, handling of the undercut parts
Mold
Type of the mold, design of each part, design of ejector, etc.
Environment
Production capacity and facilities in the manufacturing plant
Molding Machine
Capabilities of the molding machine (clamping force, injection pressure , plasticizing ability of the molding material, etc.
Condition
Molding condition or molding cycle.
Molding Process
The quality of the molded products (appearance, dimension and function) is related to various factors during the molding process. As the shape of molded products becomes complex, the factors in molding process become complicated. It is said that predicting any molding related phenomenon is difficult even though it is possible to analyze such phenomenon. Therefore, it is necessary to design the molding parts through comparison and examination of many cases. The molding process is classified into the following 5 processes.
The quality of the molded parts is closely related to these processes:
Injection Flow Process
This is a process in which plasticated molten plastics is injected into the mold cavity.
The molten plastics injected initially makes the external part of the part and that injected later makes the internal part of the part.
The molten plastics injected first influences the appearance of the part.
Injection Filling Process
This is the process in which molten plastics is injected into the mold cavity. When the injection pressure is raised, plastics sink mark is reduced. However, this would also encourage development of deformation around the gate. The increase in injection pressure would require more force to take the part out of the mold. This could lead to the development of deformations at the time of removal from mold.
Gate Seal (Gate Closure) Process
This is the process from injection completion through gate sealing (gate closure).
Holding pressure (secondary pressure) is applied during cooling and solidification of the gate; it is designed to improve the filling of the molten plastics by reducing molding shrinkage.
Cooling Process
The molten plastics within the cavity is cooled and solidified during this process while the gate is sealed (closed). The difference in cooling rate within the molten plastics would cause intense shrinkage at the thicker part of the part. This would result in a sink mark, bubbles, or residual deformation of the part.
Mold Removal Process
This is the process in which the cooled and solidified plastics is ejected from the cavity and removed from the mold. The part must be ejected evenly in relation to ejector pin position; otherwise, defective conditions such as warping, whitening, or cracking would occur.
How to Improve the Quality of the Parts…
Design of the part and the mold should be performed carefully in consideration of the following advice:
Parting line
Plain or simple curving surfaces should have parting lines to prevent the development of flashes.
Gate
It is a principle to set the gate position so that the flow of the molten plastics is well balanced and consistent.
Ejection
Determine the ejecting position so that the part can be removed uniformly. It is also recommended to make the ejection area as large as possible.
Undercut
It is preferable to design the part without any undercut, but when it is not avoidable, use a method such as slide core.
Dimension
Plastics shrinkage is caused by several factors such as the physical condition of the molding material, part dimension, molding condition, and the environment in which it is used.
We have examined each condition and selected the appropriate material, dimension and condition for molding.
Major Plastics products |
Resin |
Injection pressure [kgf/ 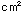 ] ] |
Resin temperature [ 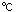 ] ] |
Mold temperature [ 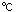 ] ] |
Plastic bags, trash bag |
Polyethylene (PE) |
600-1400 |
180-300 |
15-75 |
Interior or exterior parts of automobile |
Polypropylene (PP) |
600-1400 |
200-300 |
40-60 |
Water pipe, sewage pipe, electric pipe |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
1000-1500 |
150-180 |
35-65 |
Food containers (Clear) |
Polystyrene (PS) |
700-1700 |
180-315 |
20-60 |
Optical disk such as CD, DVD |
Polycarbonate (PC) |
800-1500 |
280-320 |
85-125 |
Acrylonitrile butadienstylene (ABS) |
700-1500 |
200-280 |
40-85 |
|
) |
Polyamide (PA) |
800-1500 |
230-300 |
20-90 |



